
| Heating method | Conditions | Power consumption |
| Induction heating | Heating 10 liters of water up to 50ºC | 0.583kWh |
| Resistance heating | Heating 10 liters of water up to 50ºC | 0.833kWh |
| Items | Induction heating | Coal-fired heating | Gas-fired heating | Resistance heating |
| Heating efficiency | 98% | 30-65% | 80% | Below 80% |
| Pollutant emissions | No noise, no dust, no exhaust gas, no waste residue | Coal cinders, smoke, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide | Carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide | Non |
| Fouling (pipe wall) | Non-fouling | Fouling | Fouling | Fouling |
| Water softener | Depending on the quality of fluid | Required | Required | Required |
| Heating stability | Constant | Power is decreased by 8% yearly | Power is decreased by 8% yearly | Power is decreased by more than 20% yearly (high power consumption) |
| Safety | Electricity and water separation, no electricity leakage, no radiation | Risk of carbon monoxide poisoning | Risk of carbon monoxide poisoning and exposure | Risk of electricity leakage, electric shock or fire |
| Durability | With core design of heating, 30 years service life | 5 years | 5 to 8 years | Half to one year |
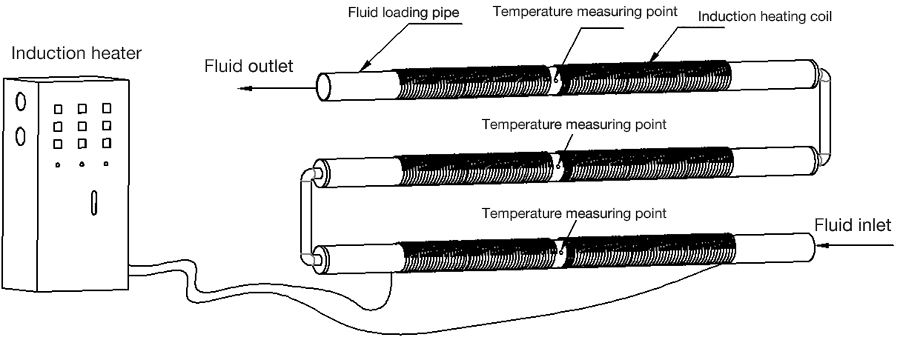
Required parameters of parts to be heated: specific heat capacity, weight, starting temperature and end temperature, heating time;
Calculation formula: specific heat capacity J/(kg*ºC)×temperature differenceºC×weight KG ÷ time S = power W
For example, to heat thermal oil of 1 ton from 20ºC to 200ºC within an hour, the power calculation is as follows:
Specific heat capacity: 2100J/(kg*ºC)
Temperature difference: 200ºC-20ºC=180ºC
Weight: 1ton=1000kg
Time: 1 hour=3600 seconds
i.e. 2100 J/ (kg*ºC)×(200ºC -20 ºC)×1000kg ÷3600s=105000W=105kW
Conclusion
The theoretical power is 105kW, but the actual power is commonly increased by 20% because of taking the heat loss into consideration, that is, the actual power is 120kW. Two sets of 60kW induction heating system as a combination are required.








